
Recovering Fraud Losses: What the Numbers Reveal

Losses from occupational fraud topped $7 billion in 2017, according to the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners’ (ACFE) most recent global study on occupational fraud and abuse, 2018 Report to the Nations. The median loss for all cases in the study was $130,000 USD, yet a full 22 percent of companies lost $1 million or more. To add insult to injury, only 15 percent of businesses that experienced fraud were able to fully recover their losses.
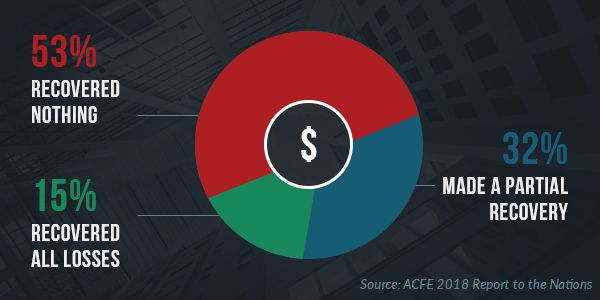
The common theme in the report is that, while it’s often worthwhile to pursue remedial action against perpetrators, victims will usually not be made whole. Here are three factors negatively impacting these recuperation efforts.
1. Failure to Report
After a fraud has been discovered and investigated, a case might proceed to prosecution, civil litigation, both, or neither. In its annual study, ACFE researchers tracked the percent of cases that were referred to law enforcement or resulted in a civil suit being filed for each year dating back to 2008. They found that the rate of criminal referrals has been gradually decreasing over that time, from 69 percent in 2008 to 58 percent in 2018. In contrast, the rate at which civil suits are filed has stayed consistent, ranging from 22 percent to 24 percent within the same timeframe.
There are many reasons why victim organizations might decide not to refer cases to law enforcement and therefore forego any additional recuperation of the loss that may result. The top five cited reasons are:
- Fear of bad publicity: 38%
- Internal discipline sufficient: 33%
- Too costly: 24%
- Private settlement: 21%
- Lack of evidence: 12%
2. The Greater the Loss, the Less Likely the Recovery
There is an inverse relationship between the amount that victim organizations lose to fraud versus what they are able to recover. So, even if the organization decides to pursue legal action, they are not likely to achieve full recovery. Here’s how the numbers panned out:
- Losses of $10,000 or less had a 30% chance of recovery
- Losses of $10,000 to $100,000 had a 16% chance of recovery
- Losses of $100,001 to $1,000,000 had a 14% chance of recovery
- Losses of $1,000,000 or more had an 8% chance of recovery
3. Desire to Avoid Fines
A third reason recovery efforts can be hampered is the knowledge that organizations may receive monetary fines from authorities for having inadequate controls in place and thus enabling fraud to occur.
Of the three types of occupational fraud – asset misappropriation, corruption, and financial statement fraud – the latter had the greatest likelihood of fines, at 17 percent. And, fines were imposed regardless of the size of the loss. For example, organizations that lost $10,000 or less were fined 14 percent of the time while those that lost $1,000,000 or more were fined 20% of the time.
At a median of $100,000 per fine, these penalties were no small matter.
An Ounce of Prevention
Given that recovery is an uphill battle, the takeaway is this: organizations should do what they can to prevent fraud from happening in the first place. Internal controls, codes of ethics, recognizing red flag behaviors, and the availability of reporting mechanisms are all tried-and-true methods for realizing that goal.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR